Regional Economic Report (Summary) (April 2014)*
- This report summarizes the reports from all regional research divisions, mainly at the Bank's branches in Japan, and is based on data and other information gathered for the meeting of general managers of the Bank's branches held today. The English translation is based on the Japanese original.
April 17, 2014
Bank of Japan
All regions reported that the economy had continued to recover or had been recovering moderately as a trend, while it had been affected by the front-loaded increase and subsequent decline in demand prior to and after the consumption tax hike. The background to these reports included the fact that domestic demand had been firm, production had been on a moderate increasing trend, and the employment and income situation had been improving.
Compared with the last assessment in January 2014, eight regions (Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto-Koshinetsu, Tokai, Kinki, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu-Okinawa) noted that their economic assessments regarding the pace of economic improvement had remained unchanged. The Hokuriku region had revised its economic assessment upward, mainly since the pick-up in business fixed investment had become increasingly evident.
| Region | Assessment in January 2014 | Changes from the previous assessment1 |
Assessment in April 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaido | The economy has been recovering moderately. | 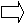 |
The economy has been recovering moderately as a trend, albeit with some fluctuations due to the consumption tax hike. |
| Tohoku | The economy has been recovering. |  |
The economy has continued to recover as a trend, albeit with some fluctuations due to the consumption tax hike. |
| Hokuriku | The economy has begun to recover moderately. | 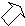 |
The economy has been recovering moderately as a trend, while it has been affected by the front-loaded increase and subsequent decline in demand prior to and after the consumption tax hike. |
| Kanto-Koshinetsu | The economy has been recovering moderately. |  |
The economy has continued to recover moderately as a trend, albeit with some fluctuations due to the consumption tax hike. |
| Tokai | The economy has been recovering. |  |
The economy has continued to recover as a trend, while the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has recently been observed. |
| Kinki | The economy has been recovering moderately. |  |
The economy has been recovering moderately as a trend, while the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has been observed. |
| Chugoku | The economy has been recovering moderately. |  |
The economy has been recovering moderately as a trend, albeit with some fluctuations due to the consumption tax hike. |
| Shikoku | The economy has been recovering moderately. |  |
The economy has continued to recover moderately as a trend, albeit with some fluctuations due to the consumption tax hike. |
| Kyushu-Okinawa | The economy has been recovering moderately. |  |
The economy has been recovering moderately as a trend, while it has been affected by the front-loaded increase and subsequent decline in demand prior to and after the consumption tax hike. |
- With regard to the changes from the previous assessment, arrows pointing to the upper right or lower right indicate changes in the pace of improvement or deterioration compared with the previous assessments, respectively. For example, an acceleration in the pace of improvement or deceleration in the pace of deterioration is indicated with an arrow pointing to the upper right. A horizontal arrow pointing to the right indicates that the pace of improvement or deterioration in economic conditions has remained unchanged compared with the previous assessments.
As for public investment, the Tohoku region reported that it was increasing significantly, and five regions (Hokkaido, Hokuriku, Kanto-Koshinetsu, Chugoku, and Shikoku) noted that it was increasing or had maintained an increasing trend. Three regions (Tokai, Kinki, and Kyushu-Okinawa) noted that it had been at a high level.
Five regions (Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto-Koshinetsu, Tokai, and Kinki) reported that business fixed investment was increasing, and four regions (Hokuriku, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu-Okinawa) noted that it was picking up or that the pick-up had become increasingly evident. Meanwhile, it was reported that business sentiment had continued to improve.
As for private consumption, with improvement in the employment and income situation, the Hokkaido region noted that it was recovering moderately, four regions (Hokuriku, Tokai, Shikoku, and Kyushu-Okinawa) reported that it was picking up moderately or picking up, and four regions (Tohoku, Kanto-Koshinetsu, Kinki, and Chugoku) noted that it had been resilient. Meanwhile, many regions reported that the front-loaded increase and subsequent decline in demand prior to and after the consumption tax hike were observed, notably in durable consumer goods (such as passenger cars and household electrical appliances) and some high-end goods.
As for sales at large retail stores, many regions reported that sales at department stores had continued to show signs of picking up or had been resilient, mainly due to firm sales of high-end goods. Several regions noted that sales at supermarkets had been more or less flat.
It was reported that automobile sales were increasing or had been resilient, partly due to the effects of the introduction of new models.
It was reported that sales of household electrical appliances were picking up or had been firm, mainly in energy-efficient white goods.
Many regions reported that travel-related demand was picking up or had been firm. Meanwhile, the Hokkaido and Kyushu-Okinawa regions noted an increase in the number of foreign visitors to Japan.
As for housing investment, five regions (Tohoku, Kanto-Koshinetsu, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu-Okinawa) reported that it was increasing or had been at a high level, assisted partly by increased orders as a result of the front-loaded increase in demand prior to the consumption tax hike. The Tokai and Kinki regions noted that it had been resilient as a trend, although the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase had been observed. On the other hand, the Hokkaido region noted that the pick-up had come to a pause.
As for production (industrial production), as a trend, four regions (Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto-Koshinetsu, and Chugoku) reported that it had continued to increase moderately, and three regions (Hokuriku, Tokai, and Kinki) noted that it had been at a high level or seemed to be firm, against the background that domestic demand had been firm, albeit with some fluctuations due to the consumption tax hike, and also that overseas demand was picking up moderately. The Shikoku region reported that production was picking up moderately, and the Kyushu-Okinawa region noted that it had been more or less flat as a whole, while progress toward an increase had been observed in some industries.
With regard to production by industry, the following trends were reported. Transportation equipment and electrical machinery were increasing or had continued to be more or less flat at a relatively high level. General-purpose, production and business oriented machinery was increasing or picking up. Metal products and ceramics, stone and clay were on an increasing trend. Electronic parts and devices was picking up or had begun to pick up. Iron and steel and chemicals had continued to be at high levels or had been more or less unchanged.
Many regions reported that the employment and income situation was improving.
Many regions reported that supply and demand conditions in the labor market were improving. As for household income, many regions noted that it was picking up or the improvement was becoming evident.
| Region | Public investment | Business fixed investment |
Private consumption |
Housing investment |
Production | Employment and income |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaido | Increasing, reflecting the effects of various economic measures | Increasing, reflecting the improvements in sales and profits amid the moderate economic recovery | Recovering moderately, on the back of improvement mainly in the employment and income situation | The pick-up has come to a pause | Increasing, against the background of the rise in demand both at home and abroad | Supply and demand conditions in the labor market are improving. Household income is recovering. |
| Tohoku | Increasing significantly, primarily in construction orders related to the restoration following the earthquake disaster | Increasing | Has been resilient | Increasing, mainly due to construction of public housing for disaster-stricken households, although the effects of the consumption tax hike have been observed | Increasing moderately | The employment and household income situation is improving |
| Hokuriku | Has maintained an increasing trend | The pick-up has become increasingly evident, particularly in manufacturing | Picking up moderately, while it has been affected by the front-loaded increase and subsequent decline in demand prior to and after the consumption tax hike | The subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has been observed | Has been at a high level | The employment and household income situation is picking up |
| Kanto-Koshinetsu | Increasing | Has been on an increasing trend | Has been resilient as a trend, albeit with some fluctuations caused by the front-loaded increase and subsequent decline in demand prior to and after the consumption tax hike | Increasing, against the background of increased orders mainly as a result of the front-loaded increase in demand prior to the consumption tax hike | Has continued to increase moderately as a trend, albeit with some fluctuations | Household income is picking up, as supply and demand conditions in the labor market continue to improve steadily |
| Tokai | Has been at a relatively high level | Increasing further | Picking up as a trend amid improvement in the employment and income situation, while the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has recently been observed | Has been resilient as a trend, although the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has been observed | Has continued to be more or less flat at a relatively high level as a trend, despite having shown some production declines in response to the subsequent decline in demand of late following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike | The employment and household income situation is improving |
| Kinki | Has been at a high level | Increasing moderately | Seems to be firm as a trend, amid improvement mainly in the employment and income situation, while the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has been observed | Seems to be firm as a trend, although the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has been observed | Seems to be firm as a trend, despite having shown some production declines due to the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike | Supply and demand conditions in the labor market are improving further. In this situation, improvement in household income is also becoming evident. |
| Chugoku | Has been on an increasing trend | Picking up | Has been resilient, while it has been affected by the front-loaded increase and subsequent decline in demand prior to and after the consumption tax hike | Increasing | Has been on a moderate increasing trend | The employment situation is improving. Household income is picking up moderately. |
| Shikoku | Increasing | Picking up | Picking up moderately | Has been at a high level | Picking up moderately | Supply and demand conditions in the labor market are improving and household income has shown signs of picking up |
| Kyushu-Okinawa | Has been at a high level | Picking up, particularly in nonmanufacturing | Has begun to pick up, assisted partly by improvement in the employment and income situation on top of favorable consumer sentiment, while the subsequent decline in demand following the front-loaded increase prior to the consumption tax hike has been observed | Has been on an increasing trend, albeit with some fluctuations due to the consumption tax hike | Has been more or less flat as a whole, while progress toward an increase has been observed in some industries | Supply and demand conditions in the labor market are improving and household income has shown signs of picking up |
Appendix: Prefectures Included in Each Region
| Region | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Hokkaido | Hokkaido |
| Tohoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, and Fukushima |
| Hokuriku | Toyama, Ishikawa, and Fukui |
| Kanto-Koshinetsu | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Niigata, Yamanashi, and Nagano |
| Tokai | Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, and Mie |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyogo, Nara, and Wakayama |
| Chugoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, and Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, and Kochi |
| Kyushu-Okinawa | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Oita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, and Okinawa |
Notice
Please contact below in advance to request permission when reproducing or copying the content of this report for commercial purposes.
Please credit the source when reproducing or copying the content of this report.
Inquiries
Regional Research Division, Research and Statistics Department
Tel : +81-3-3277-1357
